Alkali precipitation (Metal Hydroxide Precipitation)
It is the main treatment method currently used, and its use conditions are limited by the influence of environmental conditions (such as pH). This method makes use of the characteristics of amphoteric metals, which have the lowest solubility within a certain range, that is, the metals that form hydroxides have the most solid precipitation at this pH value. As the pH gets higher, the metal hydroxide precipitates and gradually dissolves in other forms in the water. The figure below shows the theoretical relationship between the pH value of each metal and metal hydroxide.
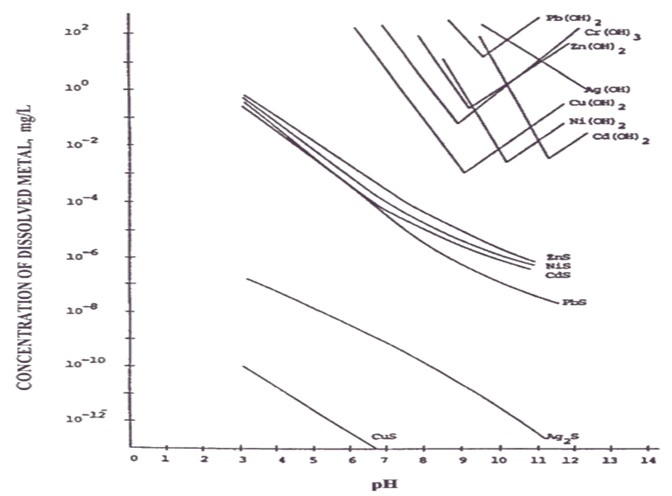
(Source: Physicochemical Treatment Processes-Handbook of Environmental Engineering)
According to this relative relationship diagram, on-site operations will consider the characteristics of individual wastewater and the presence of single or multiple metals to determine the most suitable pH range, so it is often not At the lowest point of the curve in the graph. For example, in a nickel electroplating wastewater treatment plant in Taichung, according to on-site operation experience, the optimal pH is around 11. Under this condition, the most obvious glue feathers can be produced, and the nickel concentration in the discharge water is also the lowest. The following table summarizes the optimal precipitation operating range and theoretical minimum concentration of each metal based on actual on-site experience:
| Metal type | Precipitation pH range | Minimum theoretical concentration in water (mg/L) |
| Nickel | pH 10-11 | 0.003 |
| Zinc | pH 9-10 | 0.1 |
| Copper | pH 8.5-9.5 | 0.001 |
| Chromium | pH 8.5-9.5 | 0.3 |
| Cadmium | pH 11-12 | 0.003 |
It can be seen from the table that if the theoretical minimum concentration is followed, most heavy metals can meet the 110-year release standard by relying only on the alkali precipitation method, and even reach the mainland's requirements for metal surfaces. Table 3 standards for the treatment industry (ex: Nickel <0.1ppm). However, it is actually impossible to achieve the theoretical concentration. The use of alkali precipitation method often faces the risk of excessive heavy metals for two reasons. The first is that actual wastewater treatment cannot reach the ideal state. No matter the pH adjustment, coagulation agent addition, solid-liquid separation and other procedures, it is impossible to optimize, and the theoretical concentration should not be achieved. Second, many additives are often used in each process. After the wastewater is mixed, the components in the water have become quite complex, and the various components are high and low and cannot be stable. For example, during the electroplating process, a wide variety of electroplating additives are dissolved into the wastewater. Under the interactive influence, heavy metal ions no longer simply exist in the water, but reduce the effectiveness of water treatment in various unknown forms. Therefore, when the wastewater composition is relatively complex, the alkali precipitation method is no longer a feasible and stable solution, and it is necessary to rely on other more effective treatment technologies, such as the recapture agent treatment method based on the principle of chemical precipitation.



